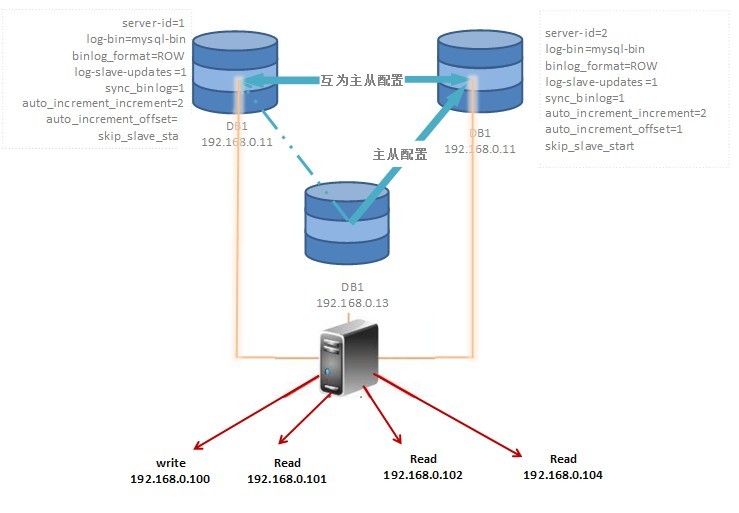
最基本的MMM安装必须至少需要2个数据库服务器和一个监控服务器下面要配置的MySQL Cluster环境包含四台数据库服务器和一台监控服务器,如下:
| function | ip | hostname | server id |
|---|---|---|---|
| monitoring host | 192.168.0.10 | mon | - |
| master 1 | 192.168.0.11 | db1 | 1 |
| master 2 | 192.168.0.12 | db2 | 2 |
| slave 1 | 192.168.0.13 | db3 | 3 |
| slave 2 | 192.168.0.14 | db4 | 4 |
如果是个人学习安装,一下子找5台机器不太容易,可以虚拟机就可以完成。
配置完成后,使用下面的虚拟IP访问MySQL Cluster,他们通过MMM分配到不同的服务器。
| ip | role | description |
|---|---|---|
| 192.168.0.100 | writer | 应用程序应该连接到这个ip进行写操作 |
| 192.168.0.101 | reader | 应用程序应该链接到这些ip中的一个进行读操作 |
| 192.168.0.102 | reader | |
| 192.168.0.103 | reader | |
| 192.168.0.104 | reader |
结构图如下:
2. Basic configuration of master 1
First we install MySQL on all hosts:
aptitude install mysql-serverThen we edit the configuration file /etc/mysql/my.cnf and add the following lines - be sure to use different server ids for all hosts:
| function | description | privileges |
|---|---|---|
| monitor user | used by the mmm monitor to check the health of the MySQL servers | REPLICATION CLIENT |
| agent user | used by the mmm agent to change read-only mode, replication master, etc. | SUPER, REPLICATION CLIENT, PROCESS |
| relication user | used for replication | REPLICATION SLAVE |
Note: We could be more restrictive here regarding the hosts from which the users are allowed to connect: mmm_monitor is used from 192.168.0.10. mmm_agent and replication are used from 192.168.0.11 - 192.168.0.14.
Note: Don't use a replication_password longer than 32 characters
4. Synchronisation of data between both databases
I'll assume that db1 contains the correct data. If you have an empty database, you still have to syncronize the accounts we have just created.
First make sure that no one is altering the data while we create a backup.
Then get the current position in the binary-log. We will need this values when we setup the replication on db2, db3 and db4.
DON'T CLOSE this mysql-shell. If you close it, the database lock will be removed. Open a second console and type:
db1$ mysqldump -u root -p --all-databases > /tmp/database-backup.sql
Now we can remove the database-lock. Go to the first shell:
(db1) mysql> UNLOCK TABLES;Copy the database backup to db2, db3 and db4.
Then import this into db2, db3 and db4:
Then flush the privileges on db2, db3 and db4. We have altered the user-table and mysql has to reread this table.
On debian and ubuntu, copy the passwords in /etc/mysql/debian.cnf from db1 to db2, db3 and db4. This password is used for starting and stopping mysql.
Both databases now contain the same data. We now can setup replication to keep it that way.
Note: Import just only add records from dump file. You should drop all databases before import dump file.
5. Setup replication
Configure replication on db2, db3 and db4 with the following commands:
Please insert the values return by “show master status” on db1 at the <file> and <position> tags.
Start the slave-process on all 3 hosts:
Now check if the replication is running correctly on all hosts:
Now we have to make db1 replicate from db2. First we have to determine the values for master_log_file and master_log_pos:
Now we configure replication on db1 with the following command:
Now insert the values return by “show master status” on db2 at the <file> and <position> tags.
Start the slave-process:
(db1) mysql> START SLAVE;Now check if the replication is running correctly on db1:
Replication between the nodes should now be complete. Try it by inserting some data into both db1 and db2 and check that the data will appear on all other nodes.
6. Install MMM
Create user
Optional: Create user that will be the owner of the MMM scripts and configuration files. This will provide an easier method to securely manage the monitor scripts.
useradd --comment "MMM Script owner" --shell /sbin/nologin mmmdMonitoring host
First install dependencies:
Then fetch the latest mysql-mmm-common*.deb and mysql-mmm-monitor*.deb and install it:
dpkg -i mysql-mmm-common_*.deb mysql-mmm-monitor*.deb
Database hosts
On Ubuntu First install dependencies:
aptitude install liblog-log4perl-perl libmailtools-perl liblog-dispatch-perl iproute libnet-arp-perl libproc-daemon-perl libalgorithm-diff-perl libdbi-perl libdbd-mysql-perlThen fetch the latest mysql-mmm-common*.deb and mysql-mmm-agent*.deb and install it:
dpkg -i mysql-mmm-common_*.deb mysql-mmm-agent_*.debOn RedHat
yum install -y mysql-mmm-agentThis will take care of all the dependencies, which may include:
Installed:
mysql-mmm-agent.noarch 0:2.2.1-1.el5
Dependency Installed:
Configure MMM
All generic configuration-options are grouped in a separate file called /etc/mysql-mmm/mmm_common.conf. This file will be the same on all hosts in the system:
<host default>
cluster_interface eth0
pid_path /var/run/mmmd_agent.pid
bin_path /usr/lib/mysql-mmm/
replication_user replication
replication_password replication_password
agent_user mmm_agent
agent_password agent_password
</host>
<host db1>
ip 192.168.0.11
mode master
peer db2
</host>
<host db2>
ip 192.168.0.12
mode master
peer db1
</host>
<host db3>
ip 192.168.0.13
mode slave
</host>
<host db4>
ip 192.168.0.14
mode slave
</host>
<role writer>
hosts db1, db2
ips 192.168.0.100
mode exclusive
</role>
<role reader>
hosts db1, db2, db3, db4
ips 192.168.0.101, 192.168.0.102, 192.168.0.103, 192.168.0.104
mode balanced
</role>
Don't forget to copy this file to all other hosts (including the monitoring host).
On the database hosts we need to edit /etc/mysql-mmm/mmm_agent.conf. Change “db1” accordingly on the other hosts:
On the monitor host we need to edit /etc/mysql-mmm/mmm_mon.conf:
<monitor>
ip 127.0.0.1
pid_path /var/run/mmmd_mon.pid
bin_path /usr/lib/mysql-mmm/
status_path /var/lib/misc/mmmd_mon.status
ping_ips 192.168.0.1, 192.168.0.11, 192.168.0.12, 192.168.0.13, 192.168.0.14
</monitor>
<host default>
monitor_user mmm_monitor
monitor_password monitor_password
</host>
debug 0
ping_ips are some ips that are pinged to determine whether the network connection of the monitor is ok. I used my switch (192.168.0.1) and the four database server.
7. Start MMM
Start the agents
(On the database hosts)
Debian/Ubuntu
Edit /etc/default/mysql-mmm-agent to enable the agent:
ENABLED=1Red Hat
RHEL/Fedora does not enable packages to start at boot time per default policy, so you might have to turn it on manually so the agents will start automatically when server is rebooted:
chkconfig mysql-mmm-agent onThen start it:
/etc/init.d/mysql-mmm-agent startStart the monitor
(On the monitoring host) Edit /etc/default/mysql-mmm-monitor to enable the monitor:
ENABLED=1Then start it:
/etc/init.d/mysql-mmm-monitor start
Wait some seconds for mmmd_mon to start up. After a few seconds you can use mmm_control to check the status of the cluster:
Because its the first startup the monitor does not know our hosts, so it sets all hosts to state AWAITING_RECOVERY and logs a warning message:
Now we set or hosts online (db1 first, because the slaves replicate from this host):