本文实例为大家分享了Python写超级马里奥的具体代码,供大家参考,具体内容如下
完整代码和素材戳我
主代码
import pygame as pg from source.main import main if __name__=='__main__': main() pg.quit()
main
__author__ = 'marble_xu'
import pygame as pg
from . import setup, tools
from . import constants as c
from .states import main_menu, load_screen, level
def main():
game = tools.Control()
state_dict = {c.MAIN_MENU: main_menu.Menu(),
c.LOAD_SCREEN: load_screen.LoadScreen(),
c.LEVEL: level.Level(),
c.GAME_OVER: load_screen.GameOver(),
c.TIME_OUT: load_screen.TimeOut()}
game.setup_states(state_dict, c.MAIN_MENU)
game.main()
setup
__author__ = 'marble_xu'
import os
import pygame as pg
from . import constants as c
from . import tools
pg.init()
pg.event.set_allowed([pg.KEYDOWN, pg.KEYUP, pg.QUIT])
pg.display.set_caption(c.ORIGINAL_CAPTION)
SCREEN = pg.display.set_mode(c.SCREEN_SIZE)
SCREEN_RECT = SCREEN.get_rect()
GFX = tools.load_all_gfx(os.path.join("resources","graphics"))
tools
__author__ = 'marble_xu'
import os
import pygame as pg
from abc import ABC, abstractmethod
keybinding = {
'action':pg.K_s,
'jump':pg.K_a,
'left':pg.K_LEFT,
'right':pg.K_RIGHT,
'down':pg.K_DOWN
}
class State():
def __init__(self):
self.start_time = 0.0
self.current_time = 0.0
self.done = False
self.next = None
self.persist = {}
@abstractmethod
def startup(self, current_time, persist):
'''abstract method'''
def cleanup(self):
self.done = False
return self.persist
@abstractmethod
def update(sefl, surface, keys, current_time):
'''abstract method'''
class Control():
def __init__(self):
self.screen = pg.display.get_surface()
self.done = False
self.clock = pg.time.Clock()
self.fps = 60
self.current_time = 0.0
self.keys = pg.key.get_pressed()
self.state_dict = {}
self.state_name = None
self.state = None
def setup_states(self, state_dict, start_state):
self.state_dict = state_dict
self.state_name = start_state
self.state = self.state_dict[self.state_name]
def update(self):
self.current_time = pg.time.get_ticks()
if self.state.done:
self.flip_state()
self.state.update(self.screen, self.keys, self.current_time)
def flip_state(self):
previous, self.state_name = self.state_name, self.state.next
persist = self.state.cleanup()
self.state = self.state_dict[self.state_name]
self.state.startup(self.current_time, persist)
def event_loop(self):
for event in pg.event.get():
if event.type == pg.QUIT:
self.done = True
elif event.type == pg.KEYDOWN:
self.keys = pg.key.get_pressed()
elif event.type == pg.KEYUP:
self.keys = pg.key.get_pressed()
def main(self):
while not self.done:
self.event_loop()
self.update()
pg.display.update()
self.clock.tick(self.fps)
def get_image(sheet, x, y, width, height, colorkey, scale):
image = pg.Surface([width, height])
rect = image.get_rect()
image.blit(sheet, (0, 0), (x, y, width, height))
image.set_colorkey(colorkey)
image = pg.transform.scale(image,
(int(rect.width*scale),
int(rect.height*scale)))
return image
def load_all_gfx(directory, colorkey=(255,0,255), accept=('.png', '.jpg', '.bmp', '.gif')):
graphics = {}
for pic in os.listdir(directory):
name, ext = os.path.splitext(pic)
if ext.lower() in accept:
img = pg.image.load(os.path.join(directory, pic))
if img.get_alpha():
img = img.convert_alpha()
else:
img = img.convert()
img.set_colorkey(colorkey)
graphics[name] = img
return graphics
运行成果
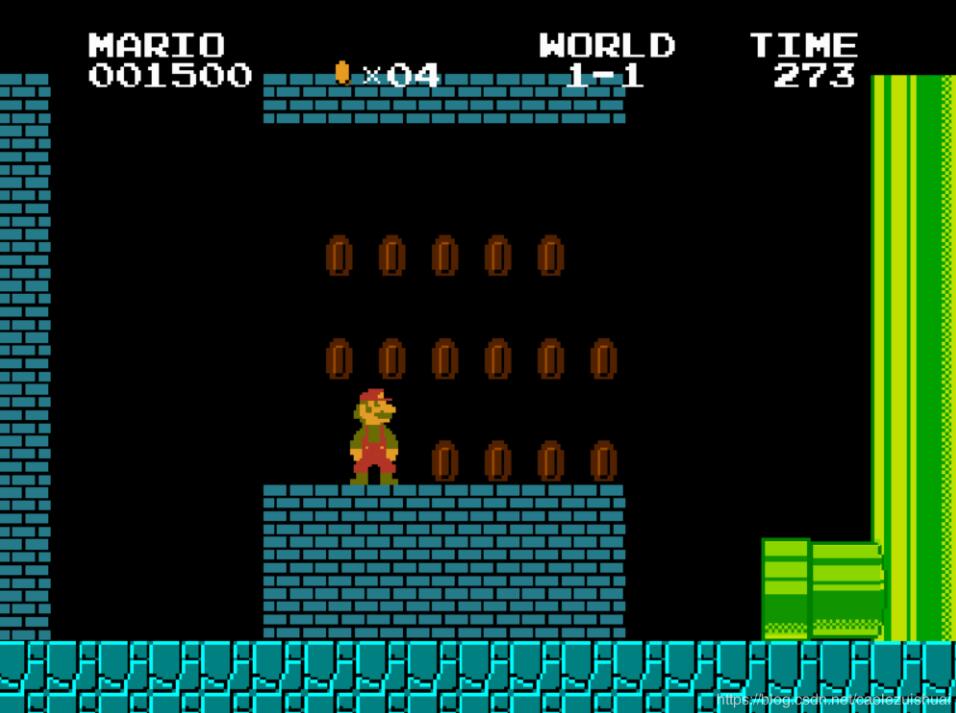

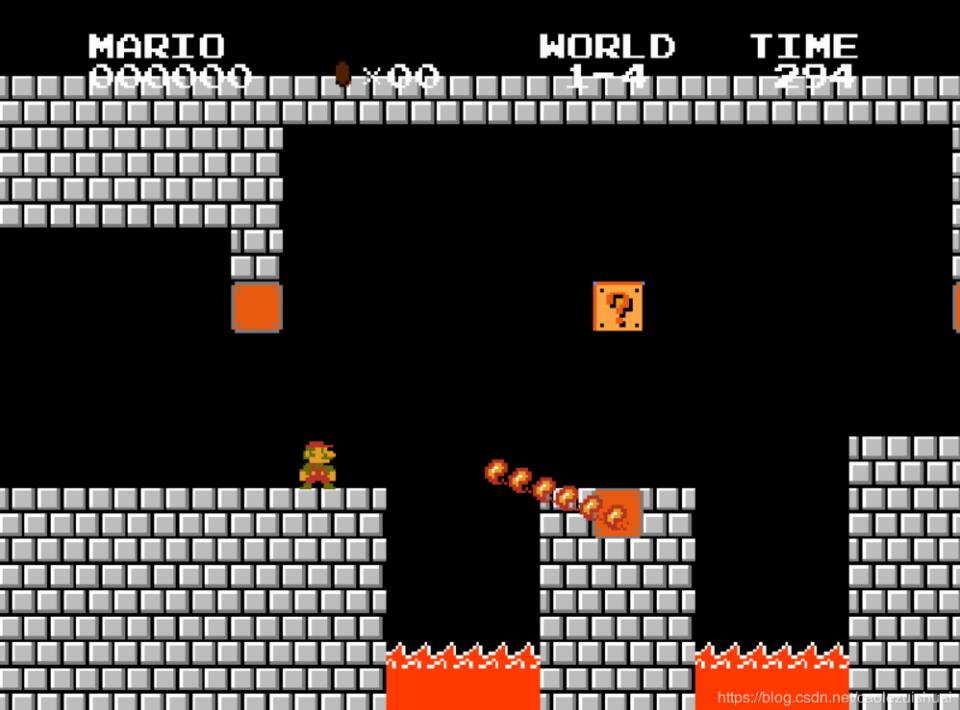
好了,被忘了在GitHub里面点star喔。
以上就是本文的全部内容,希望对大家的学习有所帮助,也希望大家多多支持脚本之家。