最近项目中需要Python的打包,看到网上也没有很详细的资料,于是做了一些示例程序。小小的研究了一下,Python如何在Windows和Linux上打包,并把程序源码以及各个记录上传到Github上与大家分享。
Python版本:3.6.8
Windows版本:Windows 10 家庭中文版 64-bit (10.0, Build 18362) (18362.19h1_release.190318-1202)
Linux版本:centos7.4
今天没时间研究cx_Freeze,先研究了一下PyInstaller。
3.1、py2exe
py2exe是一个将python转换成windows上的可独立执行的可执行程序(*.exe)的工具。不过,该可执行程序,只能在相同的Windows系统下运行,而且不适合Linux。果断被我舍弃不在研究了。
3.2、cx_Freeze
cx_Freeze 是一个类似 py2exe 的工具,但 cx_Freeze 可以在 linux 下可以直接执行的 ELF 格式的二进制可执行文件,也可以在windows上执行。
cx_Freeze的作用可以让python程序可以脱离python运行环境,在没有安装python的微型linux系统(例如cdlinux、tinycore等)里,方便地运行你的python程序。
程序简介:https://pypi.org/project/cx-Freeze/5.0/
3.3、PyInstaller
号称是目前最全面的打包程序,然后我看了一下程序更新时间。一看是10天前,嗯,不错,就它了。
程序简介:https://pypi.org/project/PyInstaller/
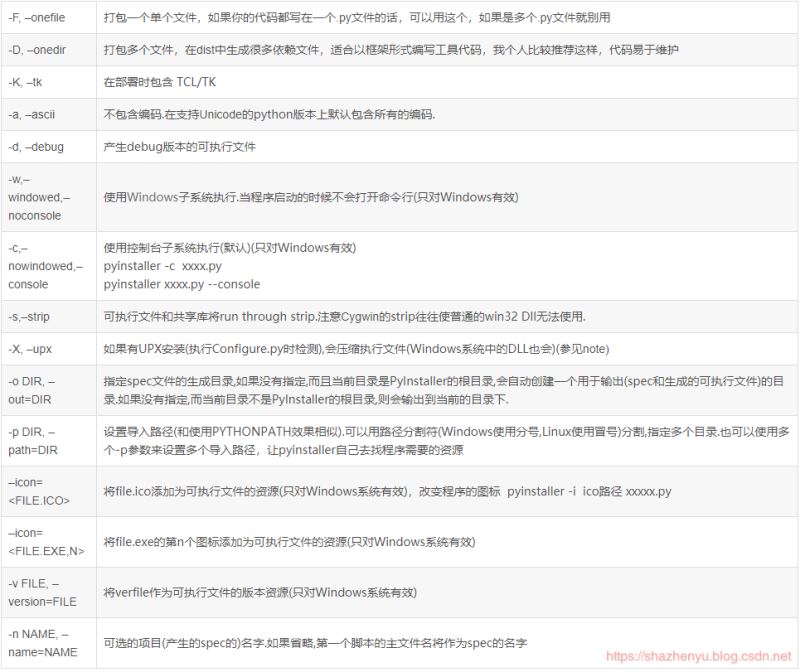
看了一下参数介绍如下:
4.1.1、核心源码
#! -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
"""
Author: ZhenYuSha
Create Time: 2020-1-20
Info: Python打包示例1,单个文件打包
“pyinstaller -F(单个可执行文件) 程序源 -n 程序名 -w(去掉控制台窗口,这在GUI界面时非常有用) -i 图标.ico”
“pyinstaller -F test1/Demo_Test1_Python.py”
"""
def bubble_sort(arr):
"""
冒泡排序
:param arr:
:return:
"""
for i in range(1, len(arr)):
for j in range(0, len(arr)-i):
if arr[j] > arr[j+1]:
arr[j], arr[j + 1] = arr[j + 1], arr[j]
return arr
if __name__ == '__main__':
test = [1, 8, 123, 18, 99, 300]
print("************************************")
print("* 冒泡排序 *")
print("************************************")
print("源列表:", test)
result = bubble_sort(test)
print("排序后:", result)
print("************************************")
input("按任意键退出...")
4.1.2、程序运行
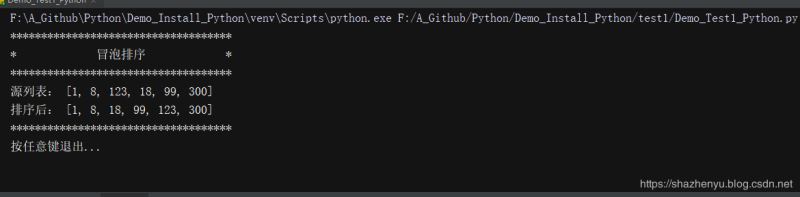
4.1.3、打包
pyinstaller -F test1/Demo_Test1_Python.py
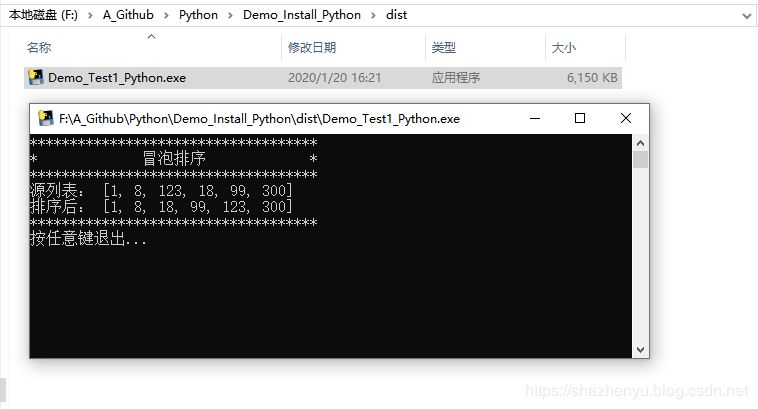
4.1.4、打包后效果
4.2.1、核心源码
#! -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
"""
Author: ZhenYuSha
Create Time: 2020-1-20
Info: Python打包示例2,多个文件打包
“pyinstaller -F(单个可执行文件) 程序源 -n 程序名 -w(去掉控制台窗口,这在GUI界面时非常有用) -i 图标.ico”
“pyinstaller -F test2/Demo_Test2_Python.py”
"""
from test2.Demo_bubble_sort import bubble_sort
from test2.Demo_heap_sort import heap_sort
if __name__ == '__main__':
test1 = [1, 8, 123, 18, 99, 300]
test2 = test1[:]
print("************************************")
print("* 两个排序 *")
print("************************************")
print("列表1 id:", id(test1))
print("列表2 id:", id(test2))
print("源列表1:", test1)
print("源列表2:", test2)
result1 = bubble_sort(test1)
result2 = heap_sort(test1)
print("冒泡后:", result1)
print("堆排后:", result2)
print("************************************")
input("按任意键退出...")
4.2.2、程序运行
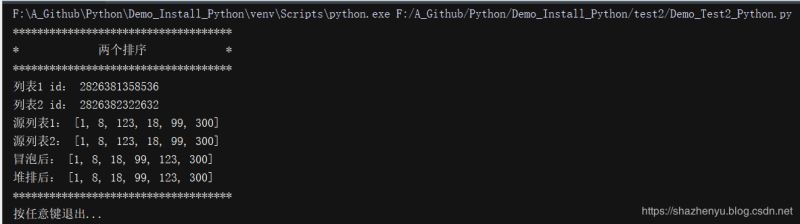
4.2.3、打包
pyinstaller -F test2/Demo_Test2_Python.py
4.2.4、打包后效果
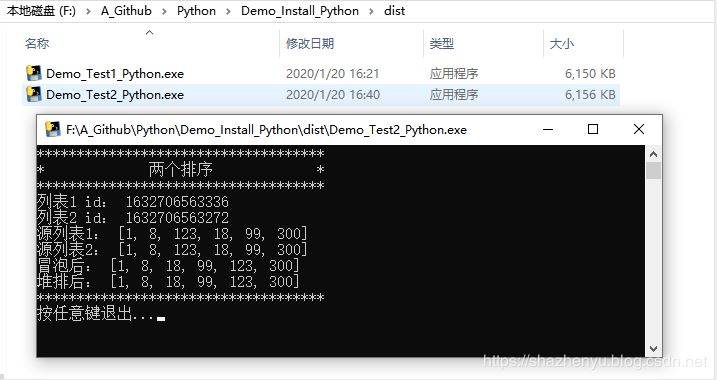
4.3.1、核心源码
#! -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
"""
Author: ZhenYuSha
Create Time: 2020-1-20
Info: Python打包示例3,多层文件打包
“pyinstaller -F(单个可执行文件) 程序源 -n 程序名 -w(去掉控制台窗口,这在GUI界面时非常有用) -i 图标.ico”
“pyinstaller -F test3/Demo_Test3_Python.py”
"""
from test3.sort.Demo_bubble_sort import bubble_sort
from test3.sort.Demo_heap_sort import heap_sort
from test3.Demo_test import Test
if __name__ == '__main__':
test1 = [1, 8, 123, 18, 99, 300]
test2 = test1[:]
print("************************************")
print("* 两个排序 *")
print("************************************")
print("列表1 id:", id(test1))
print("列表2 id:", id(test2))
print("源列表1:", test1)
print("源列表2:", test2)
result1 = bubble_sort(test1)
result2 = heap_sort(test1)
print("冒泡后:", result1)
print("堆排后:", result2)
Test.run()
print("************************************")
input("按任意键退出...")
4.3.2、程序运行
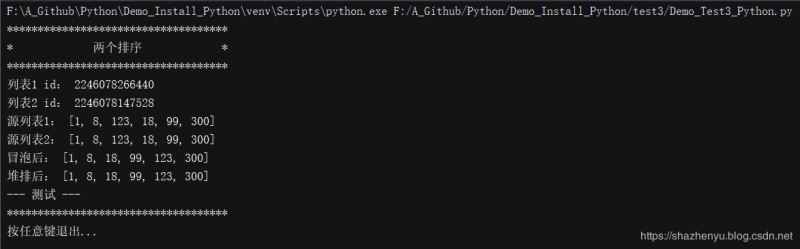
4.3.3、打包
pyinstaller -F test3/Demo_Test3_Python.py
4.3.4、打包后效果
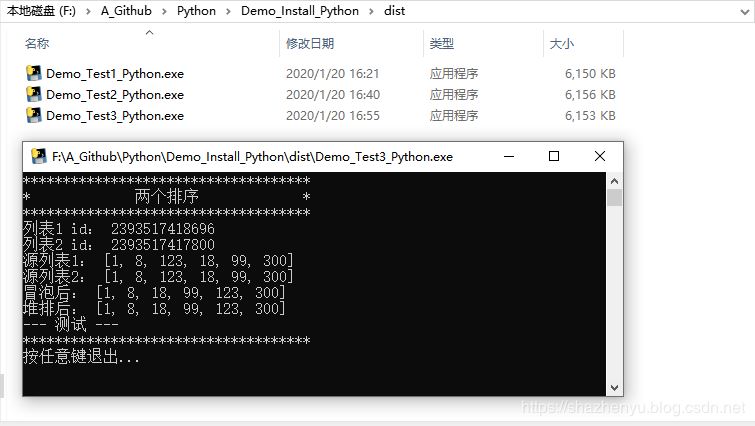
4.4.1、核心源码
#! -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
"""
Author: ZhenYuSha
Create Time: 2020-1-20
Info: Python打包示例4,多层文件打包加图标,修改程序名
“pyinstaller -F(单个可执行文件) 程序源 -n 程序名 -w(去掉控制台窗口,这在GUI界面时非常有用) -i 图标.ico”
“-p 表示自定义需要加载的类路径(一般情况下用不到)”
“pyinstaller -F test4/Demo_Test4_Python.py -n Test4 -i test4/test4.ico”
"""
from test3.sort.Demo_bubble_sort import bubble_sort
from test3.sort.Demo_heap_sort import heap_sort
from test3.Demo_test import Test
if __name__ == '__main__':
test1 = [1, 8, 123, 18, 99, 300]
test2 = test1[:]
print("************************************")
print("* 两个排序 *")
print("************************************")
print("列表1 id:", id(test1))
print("列表2 id:", id(test2))
print("源列表1:", test1)
print("源列表2:", test2)
result1 = bubble_sort(test1)
result2 = heap_sort(test1)
print("冒泡后:", result1)
print("堆排后:", result2)
Test.run()
print("************************************")
input("按任意键退出...")
4.4.2、程序运行
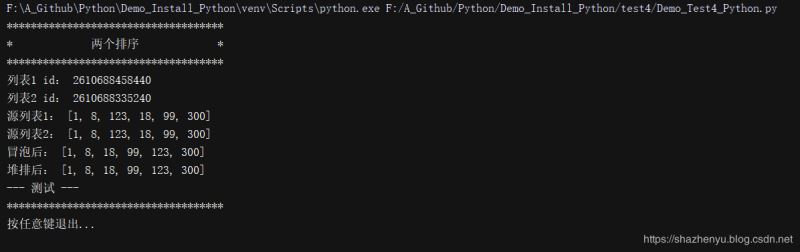
4.4.3、打包
pyinstaller -F test4/Demo_Test4_Python.py -n Test4 -i test4/test4.ico
4.4.4、打包后效果
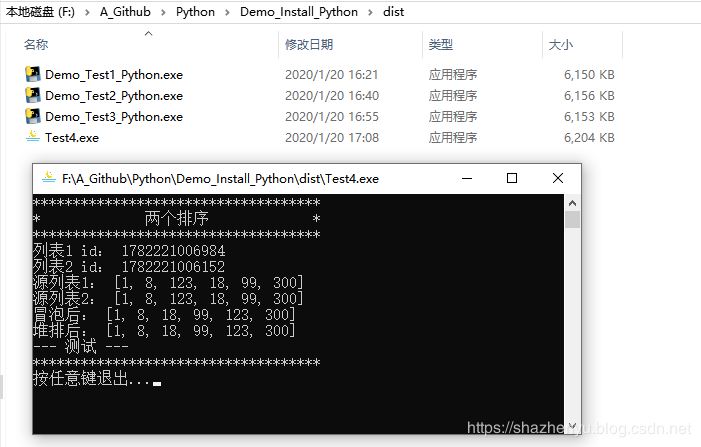
5.1.1、核心源码
#! -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
"""
Author: ZhenYuSha
Create Time: 2020-1-20
Info: Python打包示例5,多层文件打包修改程序名 linux打包
“pyinstaller -F(单个可执行文件) 程序源 -n 程序名 -w(去掉控制台窗口,这在GUI界面时非常有用) -i 图标.ico”
“-p 表示自定义需要加载的类路径(一般情况下用不到)”
“pyinstaller -F Demo_Test5_Python.py -n Test5”
"""
from sort.Demo_bubble_sort import bubble_sort
from sort.Demo_heap_sort import heap_sort
from Demo_test import Test
if __name__ == '__main__':
test1 = [1, 8, 123, 18, 99, 300]
test2 = test1[:]
print("************************************")
print("* 两个排序 *")
print("************************************")
print("列表1 id:", id(test1))
print("列表2 id:", id(test2))
print("源列表1:", test1)
print("源列表2:", test2)
result1 = bubble_sort(test1)
result2 = heap_sort(test1)
print("冒泡后:", result1)
print("堆排后:", result2)
Test.run()
print("************************************")
input("按任意键退出...")
5.1.2、程序运行
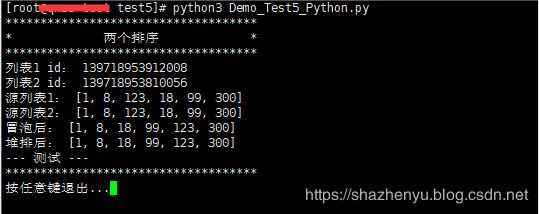
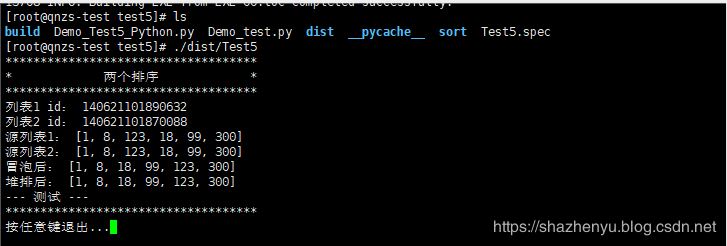
5.1.3、打包后效果
5.2.1、错误1(找不到pyinstaller)
我是用 pip install 安装的pyinstaller,于是先find了一下,找到了此命令,于是就做了个软链接。
解决方案,直接将安装目录下面的pyinstaller包作为软链接到/usr/bin下
ln -s /usr/local/python3.6.8/bin/pyinstaller /usr/bin/pyinstaller3.6
5.2.2、错误2(rebuild your Python with --enable-shared)
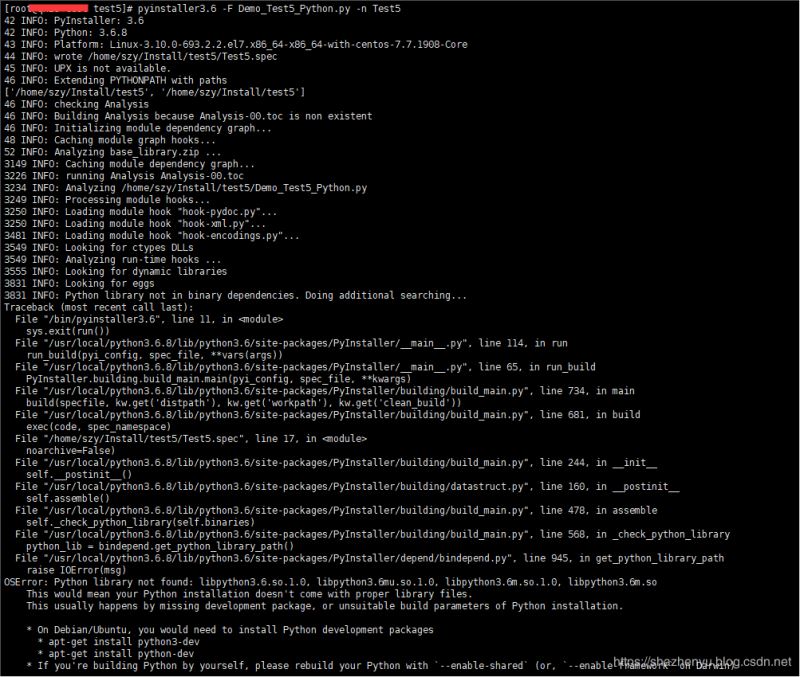
这种错误,人家已经把解决方案说出来了,就是需要重新编译嘛,那我们就按照他的来就OK了。先找到源码按照的目录,并按照以下命令操作。
./configure --prefix=/usr/local/python3.6.8(需要安装的目录) --enable-shared --with-ssl make make install

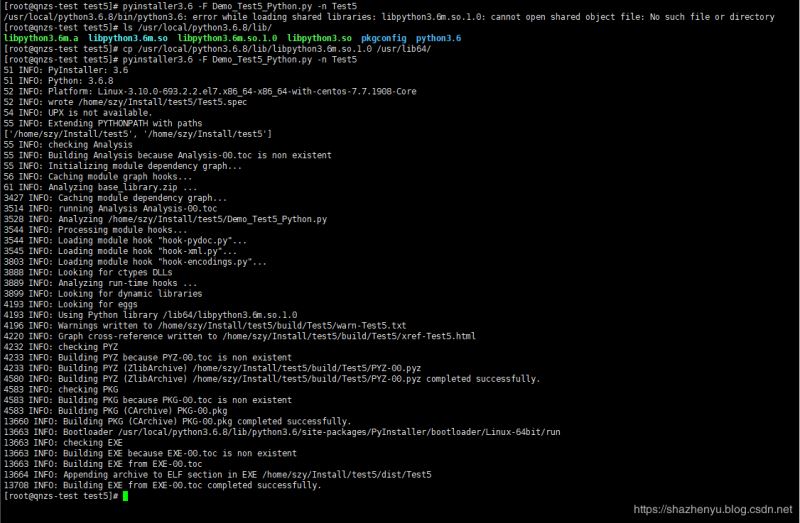
5.2.3、错误3(找不到 libpython3.6m.so.1.0)

解决方案,在安装目录找到此文件,并拷贝到/usr/lib64目录下: