一、启用远程管理
1、将管理服务器的trusthost列表改为*
运行Set-item wsman:localhost\client\trustedhosts –value *
2、在远程服务器上运行Enable-PSremoting
注:
在本地服务器上以Administrator运行“Enable-Psremoting 、 Winrm Quickconfig 、 Set-WSManQuickConfig”,均提示“访问被拒绝”,可能的原因如下:
1.在工作组计算机上,确认组策略: secpol.msc > Local Policies > Security Options > Network Access: Sharing and security model for local accounts - change to classic
2.修改注册表:Set-ItemProperty –Path HKLM:\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Policies\System –Name LocalAccountTokenFilterPolicy –Value 1 –Type DWord
3.确认WinRM服务是否正在运行,Windows Firewall服务是否正在运行,网络位置是否不是“公用”,如果要启用PS远程管理,此时网络位置不能被设置为public,因为Windows 防火墙例外不能在网络位置是public时被启用。
4.Telnet localhost 47001是否可以连通
5.运行 winrm get winrm/config 是否会提示“访问被拒绝”
6.Administrator密码不能为空
远程启用开启之后可以在cmd命令窗口输入wbemtest测试是否可以连接远程服务器,如图:
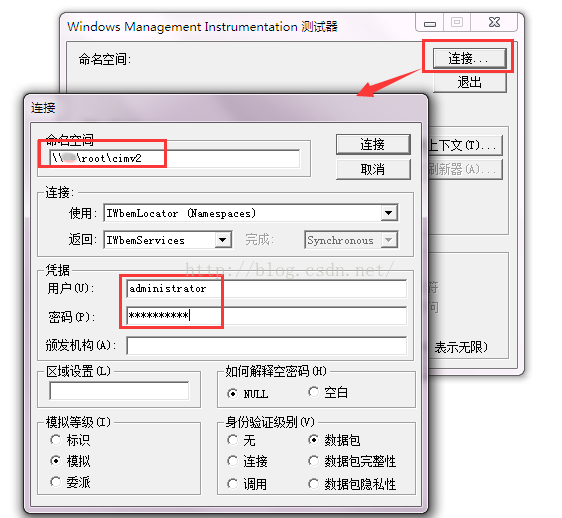
连接成功的状态如下所示:
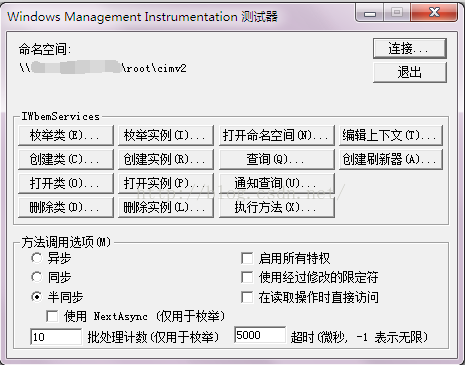
下面就可以来取每个服务器的磁盘空间了
二、脚本
$server = "."
$uid = "sa"
$db="master"
$pwd="数据库sa密码"
$mailprfname = "test" ---需要跟select name FROM msdb.dbo .sysmail_profile一致
$recipients = "接收邮箱,多个用;隔开"
$subject = "邮件标题"
$computernamexml = "E:\powershell\computername.xml"
$alter_xml = "E:\powershell\cpdisk.xml"
$pwd_xml = "E:\powershell\pwd.xml"
function GetServerName($xmlpath)
{
$xml = [xml] (Get-Content $xmlpath)
$return = New-Object Collections.Generic.List[string]
for($i = 0;$i -lt $xml.computernames.ChildNodes.Count;$i++)
{
if ( $xml.computernames.ChildNodes.Count -eq 1)
{
$cp = [string]$xml.computernames.computername
}
else
{
$cp = [string]$xml.computernames.computername[$i]
}
$return.Add($cp.Trim())
}
$return
}
function GetAlterCounter($xmlpath)
{
$xml = [xml] (Get-Content $xmlpath)
$return = New-Object Collections.Generic.List[string]
$list = $xml.counters.Counter
$list
}
function Getpwd($xmlpath)
{
$xml = [xml] (Get-Content $xmlpath)
$returnpwd = New-Object Collections.Generic.List[string]
for($i = 0;$i -lt $xml.pwd.ChildNodes.Count;$i++)
{
if ( $xml.pwds.ChildNodes.Count -eq 1)
{
$pw = [string]$xml.pwd.password
}
else
{
$pw = [string]$xml.pwd.password[$i]
}
$returnpwd.Add($pw.Trim())
}
$returnpwd
}
function CreateAlter($message)
{
$SqlConnection = New-Object System.Data.SqlClient.SqlConnection
$CnnString ="Server = $server; Database = $db;User Id = $uid; Password = $pwd"
$SqlConnection.ConnectionString = $CnnString
$CC = $SqlConnection.CreateCommand();
if (-not ($SqlConnection.State -like "Open")) { $SqlConnection.Open() }
$cc.CommandText=
" EXEC msdb..sp_send_dbmail
@profile_name = '$mailprfname'
,@recipients = '$recipients'
,@body = '$message'
,@subject = '$subject'
"
$cc.ExecuteNonQuery()|out-null
$SqlConnection.Close();
}
$names = GetServerName($computernamexml)
$pfcounters = GetAlterCounter($alter_xml)
$upwd = Getpwd($pwd_xml)
$report = ""
for($m=0;$m -lt $names.count;$m++)
{
$cp=$names[$m]
$p=New-Object -TypeName System.Collections.ArrayList
$uname="administrator"--因为取的服务器用户名都是administrator,如果每台机器不一样,可以放在XML等文件中读取
$pw=$upwd[$m]
$upassword=convertto-securestring $pw -AsplainText -force;
foreach ($pfc in $pfcounters)
{
$filter="deviceID='"+$pfc.get_InnerText().Trim()+"'"
#$Disk =get-wmiobject win32_logicaldisk -computername $cp -Filter $filter
#$counter=$Disk.Freespace/1024MB
$cred=new-object system.management.automation.PSCredential($uname,$upassword);
$counter=(get-wmiobject -credential $cred -class win32_logicaldisk -computername $cp -filter $filter).Freespace/1024MB
$total=(get-wmiobject -credential $cred -class win32_logicaldisk -computername $cp -filter $filter).Size/1024MB
#$pfc = $pfcounters[$i]
$path = "机器名:"+$cp+"; 盘符:"+$pfc.get_InnerText()
$diskFree=";总磁盘空间大小为:"+[math]::truncate($total).ToString()+"G;当前剩余空间大小为:"+[math]::truncate($counter).ToString()+"G!"
$item = "{0} {1} " -f $path,$diskFree
$report += $item + "`n"
}
}
$report
if($report -ne "")
{
CreateAlter $report
}
效果:
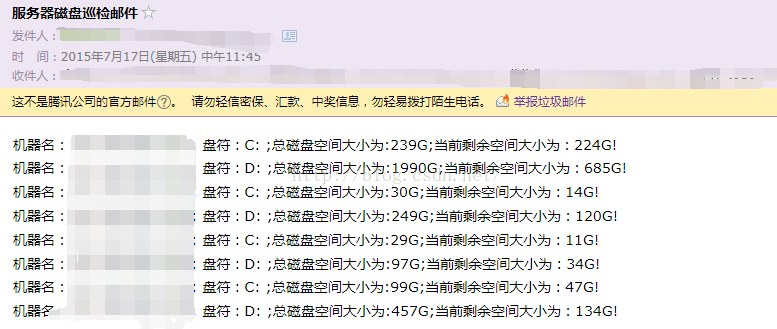
附:
xml文件格式:
1、computername.xml
<computername>
<computername>
test
</computername>
</computernames>
2、cpdisk.xml
<Counters>
<Counter>C:</Counter>
<Counter>D:</Counter>
</Counters>
3、pwd.xml
<pwd>
<password>
helloworld
</password>
<pwd>
完毕,欢迎拍砖!大笑