很多时候我们需要通过Socket发送特定的TCP请求给服务器的特定端口来实现探测服务器的指定端口所开启的服务。很多语言都有相应的方法实现上述需求,当然,PowerShell也不例外,比如我们要发送一个简单的http请求到指定的web服务器:
GET / HTTP/1.1
Host:cn.bing.com
这里我们想请求微软必应的中文首页,如果需要通过PowerShell向cn.bing.com服务器发送get请求,就需要创建一个System.Net.Sockets.TcpClient对象,向指定的服务器和端口发送请求。
具体代码如下:
[string] $output = ""
## Store the input into an array that we can scan over. If there was no input,
## then we will be in interactive mode.
$currentInput = $inputObject
if(-not $currentInput)
{
$SCRIPT:currentInput = @($input)
}
$scriptedMode = [bool] $currentInput
function Main
{
## Open the socket, and connect to the computer on the specified port
if(-not $scriptedMode)
{
write-host "Connecting to $remoteHost on port $port"
}
trap { Write-Error "Could not connect to remote computer: $_"; exit }
$socket = new-object System.Net.Sockets.TcpClient($remoteHost, $port)
if(-not $scriptedMode)
{
write-host "Connected. Press ^D followed by [ENTER] to exit.`n"
}
$stream = $socket.GetStream()
if($UseSSL)
{
$sslStream = New-Object System.Net.Security.SslStream $stream,$false
$sslStream.AuthenticateAsClient($remoteHost)
$stream = $sslStream
}
$writer = new-object System.IO.StreamWriter $stream
while($true)
{
## Receive the output that has buffered so far
$SCRIPT:output += GetOutput
## If we're in scripted mode, send the commands,
## receive the output, and exit.
if($scriptedMode)
{
foreach($line in $currentInput)
{
$writer.WriteLine($line)
$writer.Flush()
Start-Sleep -m $commandDelay
$SCRIPT:output += GetOutput
}
break
}
## If we're in interactive mode, write the buffered
## output, and respond to input.
else
{
if($output)
{
foreach($line in $output.Split("`n"))
{
write-host $line
}
$SCRIPT:output = ""
}
## Read the user's command, quitting if they hit ^D
$command = read-host
if($command -eq ([char] 4)) { break; }
## Otherwise, Write their command to the remote host
$writer.WriteLine($command)
$writer.Flush()
}
}
## Close the streams
$writer.Close()
$stream.Close()
## If we're in scripted mode, return the output
if($scriptedMode)
{
$output
}
}
## Read output from a remote host
function GetOutput
{
## Create a buffer to receive the response
$buffer = new-object System.Byte[] 1024
$encoding = new-object System.Text.AsciiEncoding
$outputBuffer = ""
$foundMore = $false
## Read all the data available from the stream, writing it to the
## output buffer when done.
do
{
## Allow data to buffer for a bit
start-sleep -m 1000
## Read what data is available
$foundmore = $false
$stream.ReadTimeout = 1000
do
{
try
{
$read = $stream.Read($buffer, 0, 1024)
if($read -gt 0)
{
$foundmore = $true
$outputBuffer += ($encoding.GetString($buffer, 0, $read))
}
} catch { $foundMore = $false; $read = 0 }
} while($read -gt 0)
} while($foundmore)
$outputBuffer
}
. Main
该脚本使用方法如下:
$http = @"
GET / HTTP/1.1
Host:cn.bing.com
`n`n
"@
$http | .\Send-TcpRequest cn.bing.com 80
执行效果如图所示:
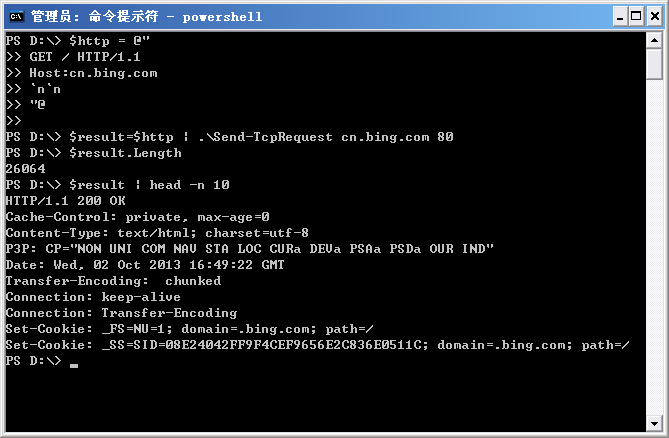
需要说明的是,由于页面返回的内容太长了,这里至少是将返回的内容缓存在一个变量里,并只输出了变量的头10行。
有了这个脚本,我们就可以向指定的web服务器发送特定的请求,来实现模拟登陆和操作的功能了。