公用表表达式简介:
公用表表达式 (CTE) 可以认为是在单个 SELECT、INSERT、UPDATE、DELETE 或 CREATE VIEW 语句的执行范围内定义的临时结果集。CTE 与派生表类似,具体表现在不存储为对象,并且只在查询期间有效。与派生表的不同之处在于,公用表表达式 (CTE) 具有一个重要的优点,那就是能够引用其自身,从而创建递归 CTE。递归 CTE 是一个重复执行初始 CTE 以返回数据子集直到获取完整结果集的公用表表达式。
下面先创建一个表,并插入一些数据:
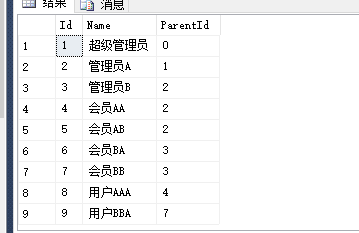
create table Role_CTE ( Id int not null, Name nvarchar(32) not null, ParentId int not null ) insert into Role_CTE(Id,Name,ParentId) select '1','超级管理员','0' union select '2','管理员A','1' union select '3','管理员B','2' union select '4','会员AA','2' union select '5','会员AB','2' union select '6','会员BA','3' union select '7','会员BB','3' union select '8','用户AAA','4' union select '9','用户BBA','7' -- 创建一个复合聚集索引 create clustered index Clu_Role_CTE_Index on Role_CTE(Id,ParentId) with ( pad_index=on, fillfactor=50, drop_existing=off, statistics_norecompute=on ) select * from Role_CTE
查找指定节点的所有子孙节点:
使用普通 sql 语句实现:
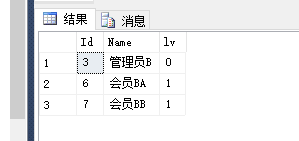
declare @level int declare @node int declare @ResTab table ( node int not null, lv int not null ) set @level=0 -- 表示初始的等级 set @node=3 --表示初始的节点ID,即从指定的哪个节点开始查找 insert into @ResTab -- 为表变量插入初始的数据 select Id,@level from Role_CTE where Id=@node while(@@ROWCOUNT>0) begin set @level=@level+1 insert into @ResTab select b.Id,@level from @ResTab a join Role_CTE b on a.node=b.ParentId and lv=@level-1 -- join 等于 inner join(内连接)和自连接 end select a.node,b.Name,a.lv from @ResTab a left join Role_CTE b on a.node=b.Id
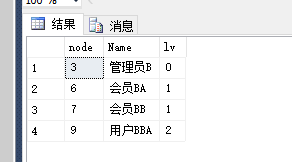
以上是根据指定节点ID(3),查找父节点ID(即字段 ParentId)等于指定的节点ID,如果有就插入,并继续循环。
PS:lv=@level-1 是重点,不然会进入死循环,作用就是限制只插入一次。
如果需要限制循环的次数,即递归的层数,那么只需要在 while 条件里面添加一个限制即可。如下:
declare @level int declare @node int declare @num int declare @ResTab table ( node int not null, lv int not null ) set @level=0 -- 表示初始的等级 set @node=3 --表示初始的节点ID,即从指定的哪个节点开始查找 set @num=1 -- 指定递归层级,即循环的次数 insert into @ResTab -- 为表变量插入初始的数据 select Id,@level from Role_CTE where Id=@node while(@@ROWCOUNT>0 and @level<@num) begin set @level=@level+1 insert into @ResTab select b.Id,@level from @ResTab a join Role_CTE b on a.node=b.ParentId and lv=@level-1 -- join 等于 inner join(内连接)和自连接 end select a.node,b.Name,a.lv from @ResTab a left join Role_CTE b on a.node=b.Id
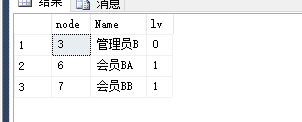
当然,如果指定了循环次数,就可以不用 while 判断语句的 @@rowcount>0 了。
使用 SQL CTE 实现:
declare @node int set @node=3; with temp_cte as ( select Id,Name,0 lv -- 查询出“根节点”,即指定的起始节点 from Role_CTE where Id=@node union all select b.Id,b.Name,a.lv+1 from temp_cte a join Role_CTE b on a.Id=b.ParentId ) select * from temp_cte
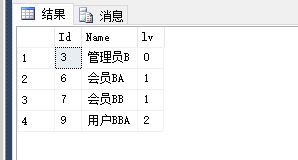
使用 CTE 控制递归的层数,与上面类似。如下:
declare @node int
declare @num int
set @node=3;
set @num=1;
with temp_cte
as
(
select Id,Name,0 lv -- 查询出“根节点”,即指定的起始节点
from Role_CTE
where Id=@node
union all
select b.Id,b.Name,a.lv+1
from temp_cte a
join Role_CTE b on a.Id=b.ParentId
and a.lv<@num --控制递归层数
)
select * from temp_cte
查找指定节点的所有祖先节点:
使用普通 sql 语句实现:
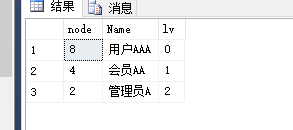
declare @level int declare @node int declare @num int declare @ResTab table ( node int not null, lv int not null ) set @level=0 -- 表示初始的等级 set @node=8 --表示初始的节点ID,即从指定的哪个节点开始查找 set @num=2 -- 指定递归层级,即循环的次数 while(@level<=@num and @node is not null) -- 如果为空就表示没有查到父级了 begin insert into @ResTab select @node,@level set @level=@level+1 select @node=ParentId from Role_CTE where Id=@node end select a.node,b.Name,a.lv from @ResTab a left join Role_CTE b on a.node=b.Id
使用 SQL CTE 实现:
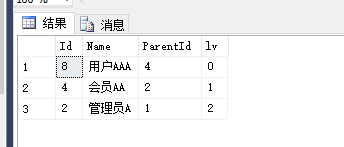
declare @node int
declare @num int
set @node=8;
set @num=2;
with temp_cte
as
(
select Id,Name,ParentId,0 lv -- 查询出“根节点”,即指定的起始节点
from Role_CTE
where Id=@node
union all
select b.Id,b.Name,b.ParentId,a.lv+1
from temp_cte a
join Role_CTE b on a.ParentId=b.Id
and a.lv < @num --控制递归层数
)
select * from temp_cte
以上所述是小编给大家介绍的SQL Server 公用表表达式(CTE)实现递归的方法,希望对大家有所帮助,如果大家有任何疑问欢迎给我留言,小编会及时回复大家的,在此也非常感谢大家对脚本之家网站的支持!