链表一直是面试的高频题,今天先总结一下单链表的使用,下节再总结双向链表的。本文主要有单链表的创建、插入、删除节点等。
1、概念
单链表是一种链式存取的数据结构,用一组地址任意的存储单元存放线性表中的数据元素。
链表中的数据是以结点来表示的,每个结点的构成:元素 + 指针,元素就是存储数据的存储单元,指针就是连接每个结点的地址数据。如下图:
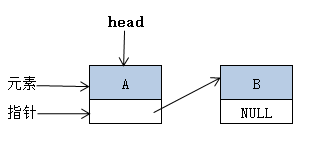
2、链表的基本操作
SingleList.cpp:
#include "stdafx.h"
#include "SingleList.h"
#include <cstdlib>
#include <iostream>
#include <string.h>
#include <conio.h>
#include <stdio.h>
/*c++实现简单的单链表操作*/
using namespace std;
SingleList::SingleList()
{
int num;
char name[128];
// 创建链表
node *stuList = CreatNode();
PrintList(stuList);
// 插入节点
printf("\n请输入要插入的学生学号和姓名,输入0 0表示结束.");
scanf_s("%d%s", &num, name, 100);
stuList = InsertNode(stuList, num, name);
PrintList(stuList);
// 删除节点
printf("\n请输入要删除的学生学号:");
scanf_s("%d", &num, 100);
stuList = DeleteNode(stuList, num);
PrintList(stuList);
// 逆序
printf("\n逆序后的链表为:\n");
stuList = ReverseList(stuList);
PrintList(stuList);
system("PAUSE");
}
SingleList::~SingleList()
{
}
//建立单链表
node *SingleList::CreatNode()
{
node *head, *p, *s;
int num = 0;
char name[128];
int cycle = 1;
head = (node *)malloc(sizeof(node)); // 为头结点分配内存空间
head->next = nullptr;
p = head; // p指向头节点
while (cycle)
{
printf("\n请输入学生的学号和姓名:");
scanf_s("%d%s", &num, name, 100);
if (num != 0)
{
s = (node *)malloc(sizeof(node));
s->num = num;
memcpy(s->name, name, 128);
printf("%d%s", s->num, s->name);
p->next = s; // 指向新插入的节点
p = s; // p指向当前节点
}
else
{
cycle = 0;
}
}
head = head->next;
p->next = NULL;
printf("头节点学生信息为: %d%s\n", head->num, head->name);
return head;
}
//单链表插入
node *SingleList::InsertNode(node *head, int num, char* name)
{
node *s, *p1, *p2 = NULL;
p1 = head;
s = (node *)malloc(sizeof(node));
s->num = num;
strcpy_s(s->name, name);
while ((s->num > p1->num) && p1->next != NULL)
{
p2 = p1;
p1 = p1->next;
}
if (s->num <= p1->num)
{
if (head == p1)
{
// 插入首节点
s->next = p1;
head = s;
}
else
{
// 插入中间节点
p2->next = s;
s->next = p1;
}
}
else
{
// 插入尾节点
p1->next = s;
s->next = NULL;
}
return head;
}
// 计算单链表长度
int SingleList::GetLength(node *head)
{
int length = 0;
node *p;
p = head;
while (p != NULL)
{
p = p->next;
length++;
}
return length;
}
//单链表删除某个元素
node *SingleList::DeleteNode(node *head, int num)
{
node *p1, *p2 = nullptr;
p1 = head;
while (num != p1->num && p1->next != NULL)
{
p2 = p1;
p1 = p1->next;
}
if (num == p1->num)
{
if (p1 == head)
{
head = p1->next;
}
else
{
p2->next = p1->next;
}
free(p1);
}
else
{
printf("找不到学号为%d 的学生!\n", num);
}
return head;
}
//单链表逆序
node *SingleList::ReverseList(node *head)
{
// A->B->C->D
node *old_head; // 原来链表的头
node *new_head; // 新链表的头
node *cur_head; // 获得原来链表的头
if (head == NULL || head->next == NULL)
return head;
new_head = head; // A
cur_head = head->next; // B
while (cur_head)
{
old_head = cur_head->next; // 将原来链表的头取出,并将第二个节点作为头节点
cur_head->next = new_head; // 将取出的头设为新链表的头
new_head = cur_head; // 新链表的头就是目前新链表的头
cur_head = old_head; // 接着处理
}
head->next = NULL;
head = new_head;
return head;
}
//打印单链表
void SingleList::PrintList(node *head)
{
node *p;
int n;
n = GetLength(head);
printf("\n打印出 %d 个学生的信息:\n", n);
p = head;
while (p != NULL)
{
printf("学号: %d ,姓名: %s\n", p->num, p->name);
p = p->next;
}
}
SingleList.h:
#pragma once
typedef struct student
{
int num; // 学号
char name[128]; // 姓名
struct student *next;
}node;
class SingleList
{
public:
SingleList();
~SingleList();
//建立单链表
node *CreatNode();
//单链表插入
node *InsertNode(node *head, int num, char* name);
// 计算单链表长度
int GetLength(node *head);
//单链表删除某个元素
node *DeleteNode(node *head, int num);
//单链表逆序
node *ReverseList(node *head);
//打印单链表
void PrintList(node *head);
};
关于逆序逻辑,研究了一下:
1、主要思路:
假设有单链表A->B->C->D,首先取出首节点A作为新逆序出来的链表
这样,原链表就为:B->C->D,逆序后的新链表为:A
2. 按照上述方法,依次取出B、C、D放入新链表
2、图形表示:
原始的单链表:
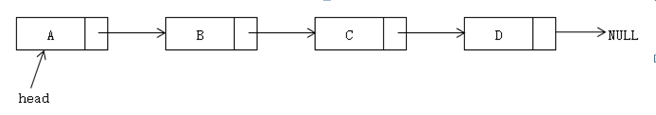
<!--[endif]-->
初始状态时,单链表如上图所示,head指向头节点A。
1. 取出原始链表的第一个节点A,然后将该节点作为新链表的头节点
原始链表:
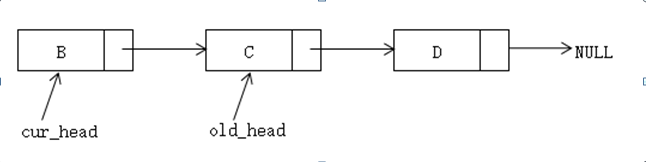
<!--[endif]-->
新链表:
<!--[if !vml]--> 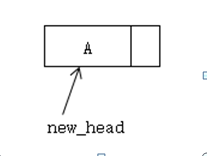 <!--[endif]-->
<!--[endif]-->
<!--[if !supportLists]--> 2.然后同上处理:
原始链表:
<!--[if !vml]--> 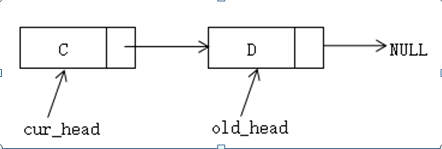 <!--[endif]-->
<!--[endif]-->
新链表:
<!--[if !vml]--> 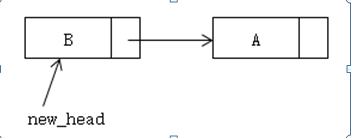 <!--[endif]-->
<!--[endif]-->
以上这篇C++ 单链表的基本操作(详解)就是小编分享给大家的全部内容了,希望能给大家一个参考,也希望大家多多支持脚本之家。